Bridging the Gap
29 Apr 2025
Hybrid Cloud Done Right: Best Practices for Flexibility, Scalability, and Efficiency
In today’s digital-first economy, large enterprises are increasingly turning to hybrid cloud as the preferred model for modern IT strategy. By combining the control and performance of on-premises infrastructure with the scalability and innovation of public cloud platforms, hybrid architectures offer the best of both worlds—allowing organisations to remain agile, compliant, and cost-efficient.
This approach is particularly suited to enterprises managing complex legacy systems, sensitive data, or regulated workloads, where full cloud adoption may not be feasible or desirable. However, building a robust hybrid cloud environment involves more than just connecting systems; it demands a strategic blend of integration, networking, security, and governance.
In this blog, I’ll explore proven best practices for designing and implementing hybrid cloud architectures. From multi-cloud-ready networks to workload optimisation and security, you’ll gain practical insights into building a future-ready hybrid environment that drives both innovation and operational excellence.
Understanding Hybrid Cloud Architecture
Hybrid cloud architecture is a computing environment that blends on-premises infrastructure with public and/or private cloud services, enabling seamless integration and workload mobility between them. It gives organisations the flexibility to run workloads where it makes the most sense—whether that’s in a local data centre for latency-sensitive applications or in the cloud for scalable analytics and burst capacity.
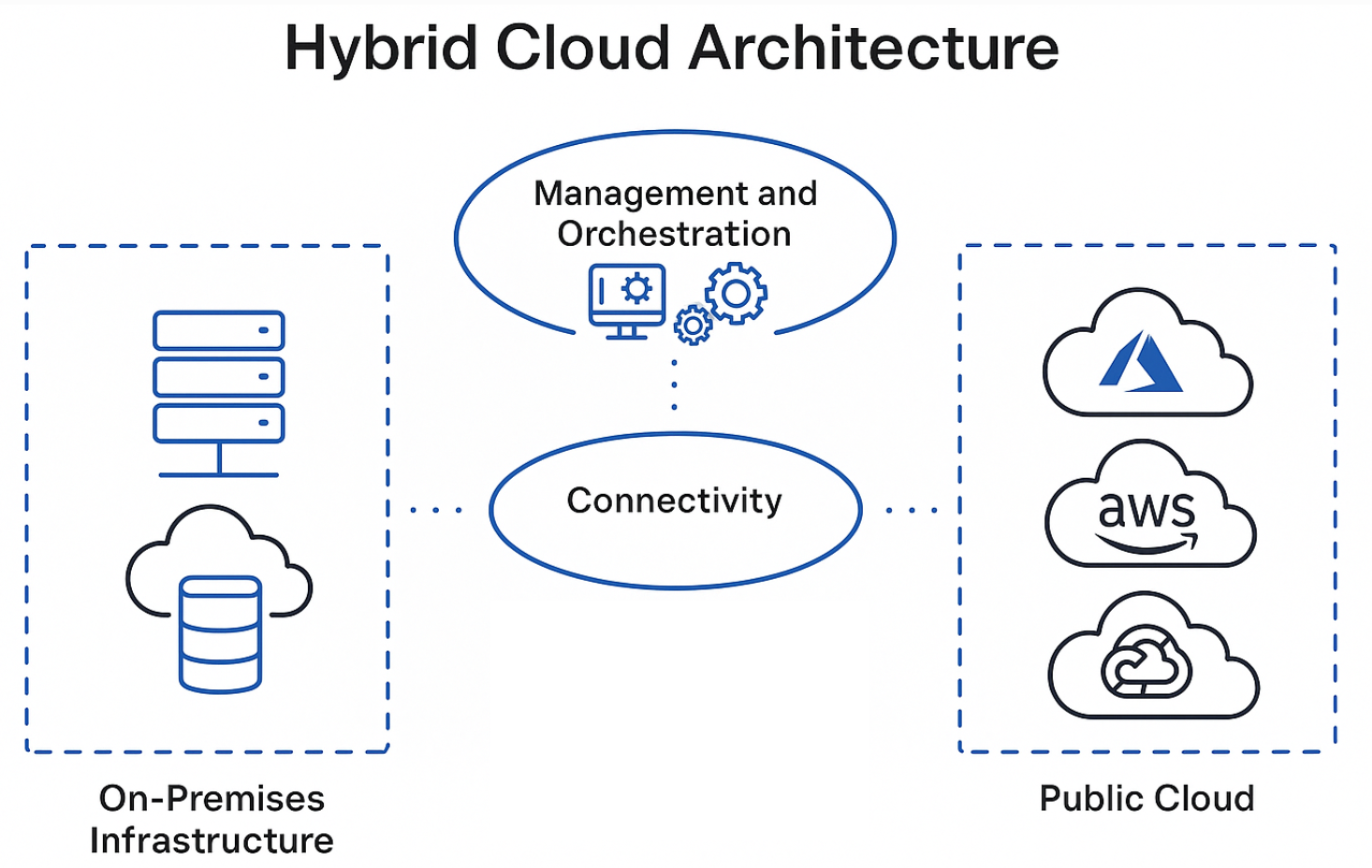
At its core, a hybrid cloud is more than just a mix of technologies—it’s a strategy that allows enterprises to modernise at their own pace, avoid vendor lock-in, and meet strict compliance or data residency requirements.
Key Components of a Hybrid Cloud Environment
- On-Premises Infrastructure: Traditional data centres or private clouds running critical or legacy workloads.
- Public Cloud Services: Elastic, on-demand compute and storage resources from providers like Microsoft Azure, AWS, or Google Cloud.
- Connectivity Layer: Secure, high-speed links (such as VPNs or ExpressRoute) enabling data and application mobility.
- Management and Orchestration Tools: Unified platforms to manage resources, monitor performance, and enforce policies across all environments.
For a comparison of environment models and more detailed discussion of hybrid cloud, see Cloud-Native vs Traditional IT Infrastructure
Strategic Considerations Before Implementation
Before diving into the technical architecture, align your hybrid cloud approach with the organisation’s strategic objectives. Start by categorising workloads based on sensitivity, latency requirements, compliance constraints, and scalability needs.
Best Practices:
- Perform a detailed workload assessment and categorisation.
- Define clear objectives for hybrid cloud use (e.g. data sovereignty, burst capacity, application modernisation).
- Align cloud usage patterns with business continuity and disaster recovery goals.
Designing for Integration and Interoperability
One of the core challenges of hybrid cloud is ensuring that applications and data can move fluidly across environments. This is particularly critical for workloads that span multiple environments or need to failover seamlessly.
Best Practices:
- Use containerisation platforms like Kubernetes to deploy portable workloads across on-prem and cloud.
- Adopt cloud-native services with hybrid capabilities, such as Azure Arc or AWS Outposts.
- Standardise APIs and service contracts for consistent communication and integration.
Building a Multi-Cloud-Ready Network
Your network is the backbone of a hybrid architecture. A robust, secure, and scalable network is essential for ensuring application performance, availability, and user experience.
Referencing Intel’s whitepaper, enterprises should focus on agility and automation in their network design.
Best Practices:
- Implement Software-Defined Networking (SDN) to enable dynamic routing and traffic optimisation.
- Leverage SD-WAN to improve connectivity across distributed sites and cloud endpoints.
- Prioritise low-latency, high-throughput links between on-premises and cloud regions.
- Design for resilience and redundancy, especially in mission-critical environments.
Security and Identity Management in a Hybrid Environment
Hybrid cloud environments can expand the attack surface if not secured properly. A consistent security model that spans identity, data protection, and access control is non-negotiable.
Best Practices:
- Implement a unified Identity and Access Management (IAM) solution such as Entra ID or Okta.
- Enforce Zero Trust principles: never trust, always verify—especially across network boundaries.
- Use encryption in transit and at rest across all environments.
- Apply centralised policy management and automate compliance checks using tools like Azure Policy or AWS Config
Monitoring and Automation
Visibility is key to managing performance, cost, and security across hybrid platforms. Without proper observability, hybrid cloud can quickly become fragmented and inefficient.
Best Practices:
- Use cloud-native monitoring tools with hybrid support (e.g. Azure Monitor, Prometheus, Grafana, Datadog).
- Implement Infrastructure as Code (IaC) using tools like Terraform or Bicep for consistent deployments.
- Automate patching, scaling, and backup operations across environments.
- Set up real-time alerts and automated remediation workflows.
Cost Optimisation and Control
Hybrid cloud offers cost flexibility—but only with proper oversight. Without controls, resources can be over-provisioned or underutilised, eroding savings.
Best Practices:
- Right-size workloads continuously using performance insights.
- Monitor spend across platforms with consolidated tools (e.g. Azure Cost Management + AWS Cost Explorer).
- Use reserved instances or capacity reservations for predictable workloads, and spot instances for batch jobs.
- Periodically audit unused or orphaned resources and shut them down.
Future Trends in Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid cloud isn’t a static model—it’s evolving to include edge computing, AI-driven automation, and serverless functions that operate closer to users and data sources.
Best Practices:
- Incorporate edge-ready infrastructure and consider use cases like real-time analytics and IoT.
- Evaluate hybrid-compatible AI/ML platforms such as Azure ML, Amazon SageMaker, or Google Vertex AI.
- Stay up to date with architectural patterns like event-driven design and microservices that scale across hybrid setups.
Conclusion
Hybrid cloud is no longer a transitional state, but a deliberate and strategic architecture choice for enterprises seeking the agility of cloud without relinquishing control of critical systems. When thoughtfully designed, a hybrid approach enables organisations to innovate faster, respond to market demands, and optimise operational efficiency - all while maintaining compliance and security.
By focusing on seamless integration, robust networking, unified security, and intelligent automation, you can build a hybrid cloud environment that’s flexible, scalable, and future-proof.